Page 314 - SAMRC Annual Report 2024-2025
P. 314
ANNUAL FINANCIAL STATEMENTS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 MARCH 2025
NOTES TO THE ANNUAL FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(CONTINUED)
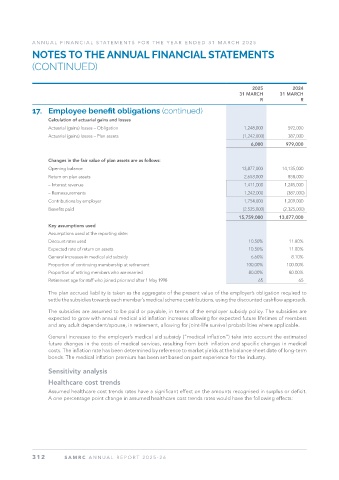
2025 2024
31 MARCH 31 MARCH
R R
17. Employee benefit obligations (continued)
Calculation of actuarial gains and losses
Actuarial (gains) losses – Obligation 1,248,000 592,000
Actuarial (gains) losses – Plan assets (1,242,000) 387,000
6,000 979,000
Changes in the fair value of plan assets are as follows:
Opening balance 13,877,000 14,135,000
Return on plan assets 2,653,000 858,000
– Interest revenue 1,411,000 1,245,000
– Remeasurements 1,242,000 (387,000)
Contributions by employer 1,754,000 1,209,000
Benefits paid (2,525,000) (2,325,000)
15,759,000 13,877,000
Key assumptions used
Assumptions used at the reporting date:
Discount rates used 10.50% 11.80%
Expected rate of return on assets 10.50% 11.80%
General increases in medical aid subsidy 6.60% 8.10%
Proportion of continuing membership at retirement 100.00% 100.00%
Proportion of retiring members who are married 80.00% 80.00%
Retirement age for staff who joined prior and after 1 May 1998 65 65
The plan accrued liability is taken as the aggregate of the present value of the employer’s obligation required to
settle the subsidies towards each member’s medical scheme contributions, using the discounted cashflow approach.
The subsidies are assumed to be paid or payable, in terms of the employer subsidy policy. The subsidies are
expected to grow with annual medical aid inflation increases allowing for expected future lifetimes of members
and any adult dependent/spouse, in retirement, allowing for joint-life survival probabilities where applicable.
General increases to the employer’s medical aid subsidy (“medical inflation”) take into account the estimated
future changes in the costs of medical services, resulting from both inflation and specific changes in medical
costs. The inflation rate has been determined by reference to market yields at the balance sheet date of long-term
bonds. The medical inflation premium has been set based on past experience for the industry.
Sensitivity analysis
Healthcare cost trends
Assumed healthcare cost trends rates have a significant effect on the amounts recognised in surplus or deficit.
A one percentage point change in assumed healthcare cost trends rates would have the following effects:
312 SAMRC ANNUAL REPOR T 2025-26